Introduce
스프링에서 비동기 처리를 위해 흔히 `@Async` 를 사용하곤 한다.
나 역시 프로젝트에서 `@Async` 를 적용하여 일부 후속 로직들을 메인 로직과 분리하여 실행하고 있었다.
그런데 얼마 전 면접장에서 다음과 같은 질문을 받았다.
@Async 로 실행된 메서드에서 예외가 발생하면 어떻게 처리하나요?
혹시 CompletableFuture 를 사용해본 경험이 있으신가요?
나는 이 질문에 대해 명확하게 답변하지 못하였다. 제대로 답변하지 못하는 모습을 보니 스스로 내가 비동기에 대해서 잘 모르고 사용하는 구나라는 생각이 들었고, `CompletableFuture` 이 무엇인지 이해해보는 시간을 가지게 되었다.
이번 글에서는 java의 기본 비동기 처리 도구인 Future 를 알아보고, 이를 보완하기 위해 나온 `CompletableFuture` 가 어떤 특징을 가지고 있는지 함께 정리해보겠다.
Future 와 CompletableFuture
java5 부터 Future 인터페이스를 통해 비동기 프로그래밍이 가능해졌다.
public Future<String> readUser() {
return executorService.submit(() -> {
Thread.sleep(2000);
return "WooJJam";
});
}하지만 해당 인터페이스는 여러가지의 단점이 존재한다.
1. 여러 연산을 결합하기 어려움.
2. 비동기 처리 중 발생하는 예외를 핸들링하기 어려움
3. 결과 수신 시 블로킹
이러한 문제점들로 인해서 실제로 해당 인터페이스를 적용하기에는 어려웠다. 따라서 이를 개선한 `CompletableFuture` 가 `java 8` 부터 등장하게 되었다.
`CompletableFuture` 클래스는 `Future` 와 `CompletionStage` 를 구현하고 있다.
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> { ... }
- `Future` : java5에서 추가된 비동기 연산을 위한 인터페이스
- `CompletionStage` : 비동기 연산의 단계를 표현하는 인터페이스로 연산의 결과를 받아서 후속 작업을 정의하는 방식의 인터페이스
`CompletableFuture` 는 `Future` 의 문제를 개선하기 위해서 등장한 만큼 여러 연산을 결합할 수 있고, 예외 처리도 가능하며 Non-Blocking도 적용할 수 있다.
Task Execution
비동기 작업을 실행하기 위해서 값을 반환하는 `supplyAsync` 와 반환값이 없는 `runAsync` 2가지 메서드가 있다.
📌 supplyAsync

`supplyAsync` 는 `Supplier`를 인자로 받는다. 그리고 내부적으로 `ForkJoinPool.commonPool` 에서 작업을 실행하고, 그 결과를 `CompletableFutrue` 객체에 담아 반환하게 된다.
만약 `Executor` 를 직접 넘기면 내가 정의한 스레드풀에서 실행되도록 변경할 수도 있다.
@Test
@DisplayName("supplyAsync로 주문 정보 실행 테스트")
void orderItemSupplyAsyncTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> orderItem(orderNo));
assertThat(future.get()).isEqualTo("iPhone 16");
}📌 runAsync

`runAsync`는 `Runnable`을 인자로 받는다. 그러므로 값을 반환하지 않고 실행만 하는 함수를 받고, `ForkJoinPool.commonPool` 에서 작업을 실행하고, 작업이 완료되면 `Void` 가 반환된다.
@Test
@DisplayName("runAsync로 주문 정보 실행 테스트")
void orderItemAsyncTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
orderItem(orderNo);
});
future.get();
}
Callback Handling
또한 `CompletableFuture`를 사용할 경우 비동기 작업이 끝난 뒤 어떤 후속 작업을 수행할지를 정의할 수 있다. 이때 사용하는 메서드가 `thenApply`, `thenAccept`, `thenRun` 3가지 메서드이다.
📌 thenApply
thenApply 메서드는 반환 값을 인수로 사용하고, 전달한 `Function`을 다음 연산으로 사용하여 새로운 값을 반환한다.

1. thenApply(Function<T, R>)
- 앞선 작업이 완료되면 현재 스레드 (ForkJoinPool, main 스레드)에서 후속 작업을 실행
- 동기 방식
@Test
@DisplayName("thenApply로 콜백 조합하기")
void thenApplyTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> orders = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> orderItem(orderNo));
CompletableFuture<String> paymentInfo = orders.thenApply(this::getPaymentInfo);
assertThat("주문 아이템: iPhone 16, 주문 가격: 1,300,000").isEqualTo(paymentInfo.get());
}
2. thenApplyAsync(Function<T, R>)
- 공용 쓰레드풀(ForkJoinPool.commonPool) 에서 비동기로 후속 작업을 실행
- 별도 스레드에서 처리됨
@Test
@DisplayName("thenApplyAsync로 콜백 조합하기")
void thenApplyAsyncTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> orders = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> orderItem(orderNo));
CompletableFuture<String> applyPaymentInfo = orders.thenApply(this::getPaymentInfo);
CompletableFuture<String> applyAsyncPaymentInfo = orders.thenApplyAsync(this::getPaymentInfo);
assertThat("주문 아이템: iPhone 16, 주문 가격: 1,300,000").isEqualTo(applyPaymentInfo.get());
assertThat("주문 아이템: iPhone 16, 주문 가격: 1,300,000").isEqualTo(applyAsyncPaymentInfo.get());
}해당 테스트 코드를 실행해보면
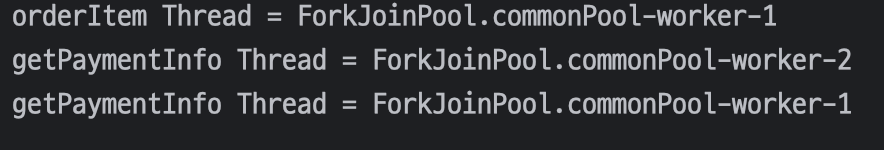
다음과 같이 `getPaymentInfo` 메서드가 서로 다른 스레드에서 실행된것을 확인할 수 있다.
3. thenApplyAsync(Function<T, R>, Executor)
- 직접 지정한 Executor에서 후속 작업을 실행
@Test
@DisplayName("thenApplyAsync 커스텀 스레드 풀로 콜백 조합하기")
void thenApplyAsyncExecutorTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
CompletableFuture<String> orders = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> orderItem(orderNo))
.thenApplyAsync(this::getPaymentInfo, executor);
assertThat("주문 아이템: iPhone 16, 주문 가격: 1,300,000").isEqualTo(orders.get());
}📌 thenAccept
thenAccept 메서드는 `Consumer` 를 인자로 받고, 결과로 `CompletableFuture<Void>` 를 반환한다.
즉, 값을 반환하지 않는 콜백이다.
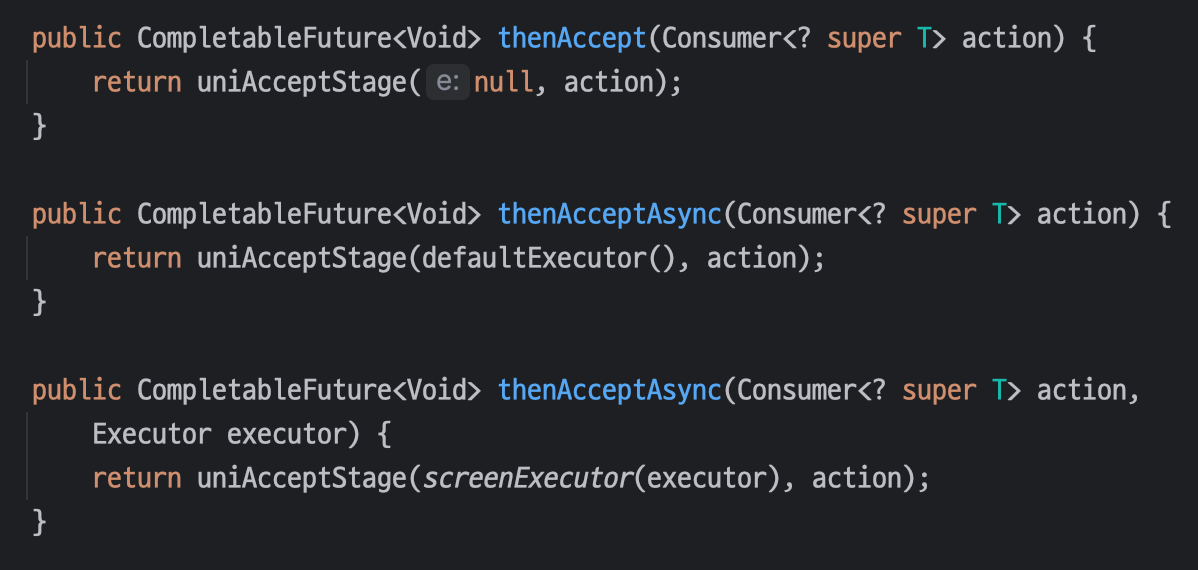
`thenApply` 와 동일하게 3가지 메서드가 있지만 큰 개념은 비슷하기에 `thenAccept` 만 알아보자.
@Test
@DisplayName("thenAccept로 콜백 조합하기")
void thenAcceptTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Void> orderFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> orderItem(orderNo))
.thenAccept(this::printOrderItem);
orderFuture.get();
}
private void printOrderItem(final String orderNo) {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("orderItem Thread = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e.getCause().getMessage());
}
System.out.println("주문 아이템: iPhone 16, 주문 가격: 1,300,000");
}
해당 테스트 코드를 살펴보면 `thenAccept` 를 사용하니 `CompletableFuture<Void>` 가 반환되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
📌 thenRun
thenRun 메서드는 `Runnable`을 인자로 받고, `thenAccept` 메서드와 동일하게 `CompletableFuture<Void>` 를 반환한다. 하지만 이전과는 다르게 이전 반환 값을 받지 않고, 그냥 다른 작업을 실행하는 콜백 메서드이다.
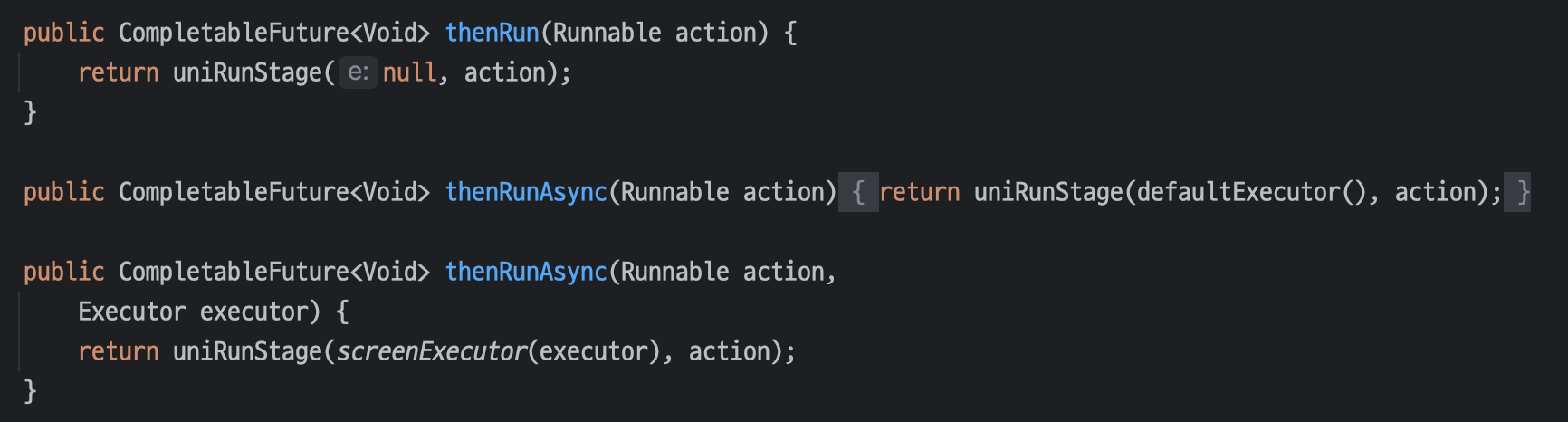
테스트 코드를 작성해보면
@Test
@DisplayName("thenRun 콜백 조합하기")
void thenRunTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Void> orderFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> orderItem(orderNo))
.thenRun(this::printOrderLog);
orderFuture.get();
}
이전 값을 인자로 주지 않고 해당 메서드를 사용할 수 있다.
Task Composition
비동기 프로그래밍에서는 종종 여러가지의 작업을 순차적으로 또는 병렬적으로 결합해야할 때가 많다. Java5의 `Future` 인터페이스에서는 처리하기 어려웠던 기능을 `CompletableFuture`로 처리할 수 있다.
📌 thenCompose
thenCompose 메서드는 이전 작업의 결과를 바탕으로 또 다른 비동기 작업을 호출할때 사용한다.
Java의 `flatMap`과 같은 개념이다.
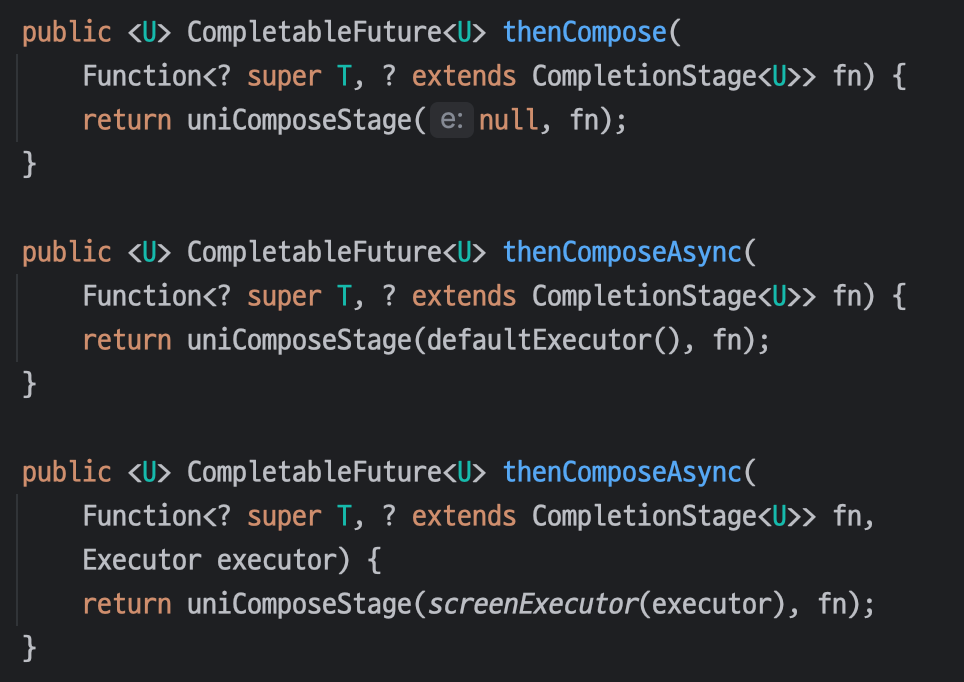
메소드 시그니처를 보면 해당 메소드 또한 비동기를 지원한다는 것을 알 수 있으며 인자로 이전 단계의 결과(`CompletionStage`)를 받는 것을 알 수 있다.
@Test
@DisplayName("thenCompose 으로 작업 결합하기")
void thenComposeTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> orderFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> orderItem(orderNo));
CompletableFuture<String> result = orderFuture.thenCompose(
item -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> getPaymentInfo(item)));
assertThat("주문 아이템: iPhone 16/ 결제 정보: 신용카드 1,200,000원").isEqualTo(result.get());
}
private String orderItem(final String orderNo) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("orderItem Thread = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e.getCause().getMessage());
}
return String.format("주문 아이템: %s", items.get(orderNo));
}
private String getPaymentInfo(final String orderItem) {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("getPaymentInfo Thread = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e.getCause().getMessage());
}
return orderItem + "/ 결제 정보: 신용카드 1,200,000원";
}
주문이 완료 되고, 결제 정보를 조회하는 메서드가 순차적으로 실행되는것을 확인할 수 있다.
📌 thenCombine
thenCombine 메서드는 서로 독립적인 `Future`이 완료된 후 결과를 함께 사용하고 싶을때 사용한다.

메서드 시그니처를 보면 `Future` 와 `BiFunction`을 인자로 받는 것을 볼 수 있다.
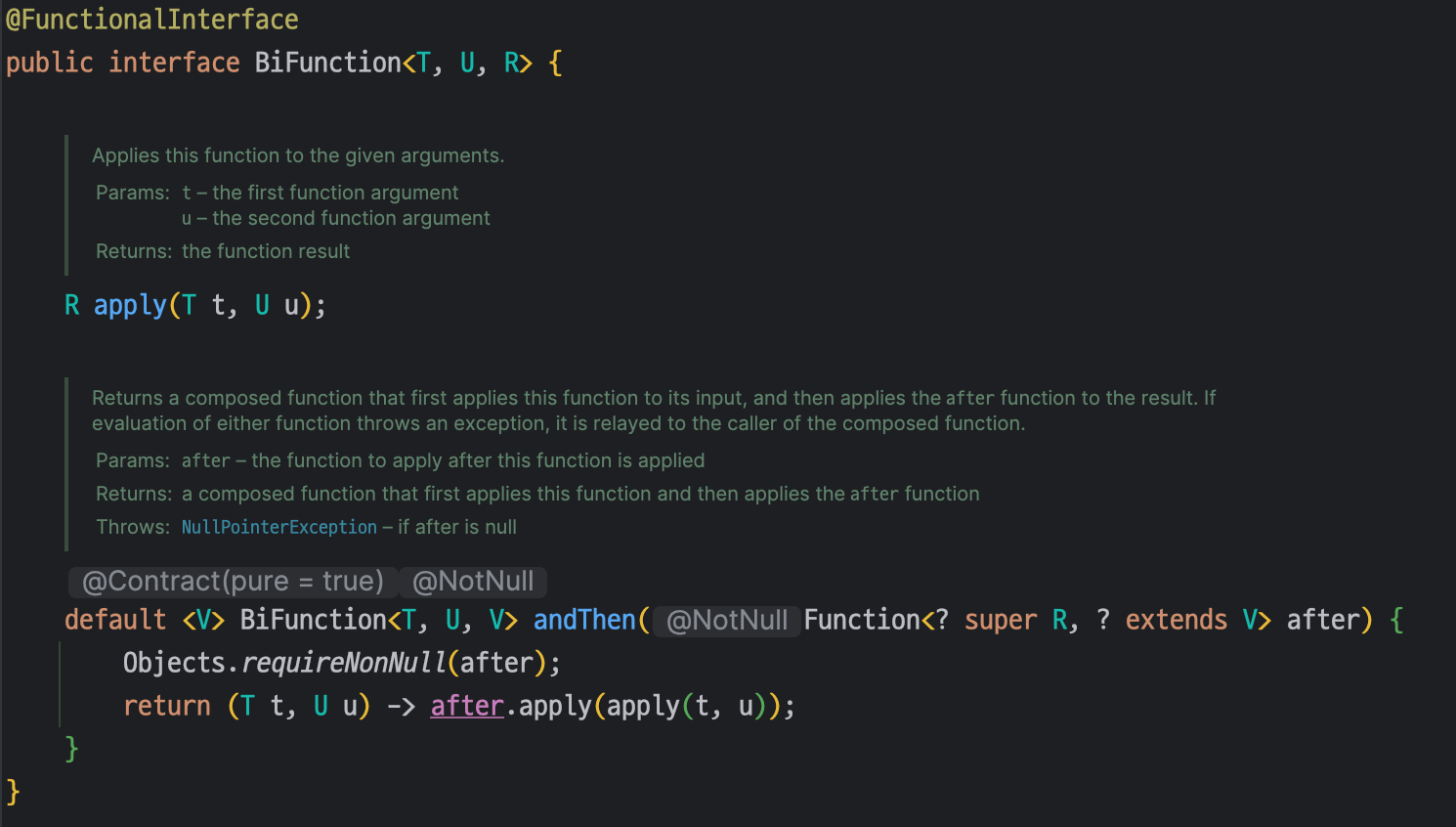
`BiFunction` 인터페이스는 T와 U 타입의 입력값을 통해서 하나의 출력값인 R을 반환하는 함수형 인터페이스이다.
@Test
@DisplayName("thenCombine 으로 작업 결합하기")
void thenCombineTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> orderFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> orderItem(orderNo));
CompletableFuture<String> optionFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(this::getProductInfo);
CompletableFuture<String> result = orderFuture.thenCombine(optionFuture,
this::combineOrderAndProductInfo);
assertThat("주문 아이템: iPhone 16/ [옵션] AppleCare+").isEqualTo(result.get());
}
private String getProductInfo() {
return "AppleCare+";
}
private String combineOrderAndProductInfo(String orderNo, String product) {
return orderNo + "/ [옵션] " + product;
}따라서 이를 테스트 코드에서 살펴보면 상품 주문과 옵션 정보를 조회하는 두개의 `Future`을 비동기로 실행하고, `thenCombine` 을 통해서 두 작업의 결과를 `combineOrderAndProductInfo` 메서드를 통해서 하나의 결과값으로 반환한다.
📌 thenAcceptBoth
thenAcceptBoth 메서드는 `thenCombine`과 비슷하지만 두 작업이 완료된 후 결과를 받아서 실행만 하고, 새로운 값을 만들 필요 없을 때 사용된다. 즉, `thenCombine` 은 값을 반환하지만 `thenAcceptBoth` 는 반환 없이 처리만 한다.
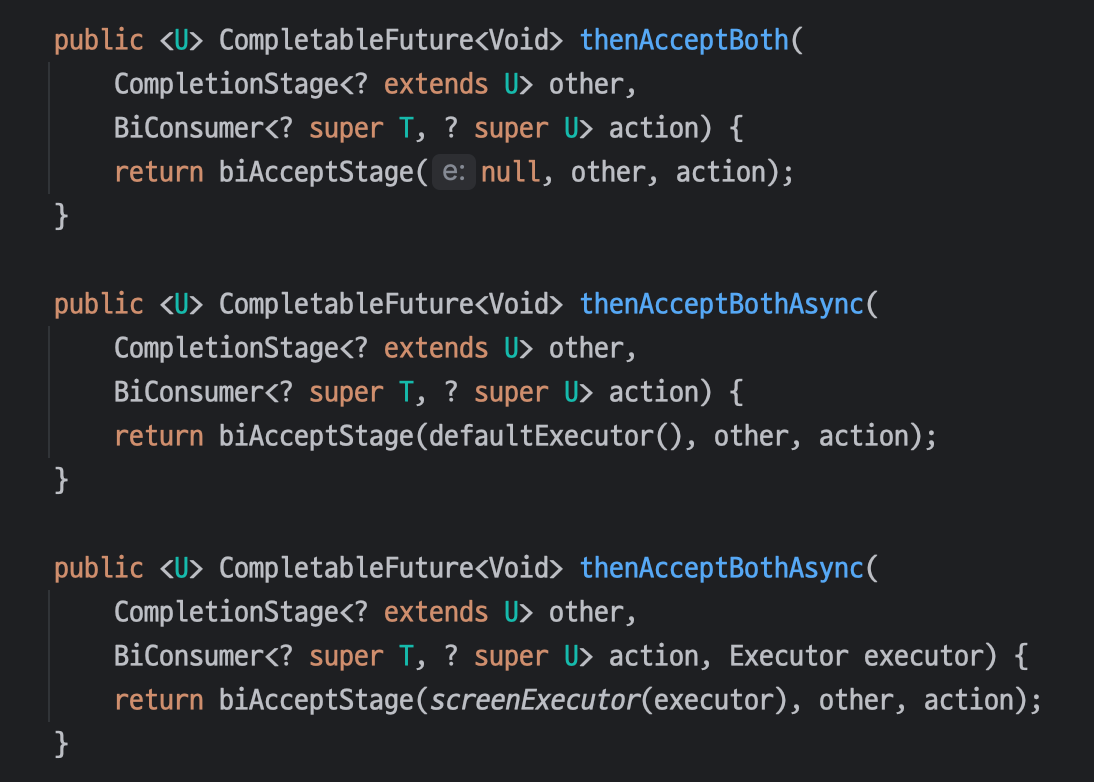
`Future` 와 `BiConsumer` 를 인자로 받는다.
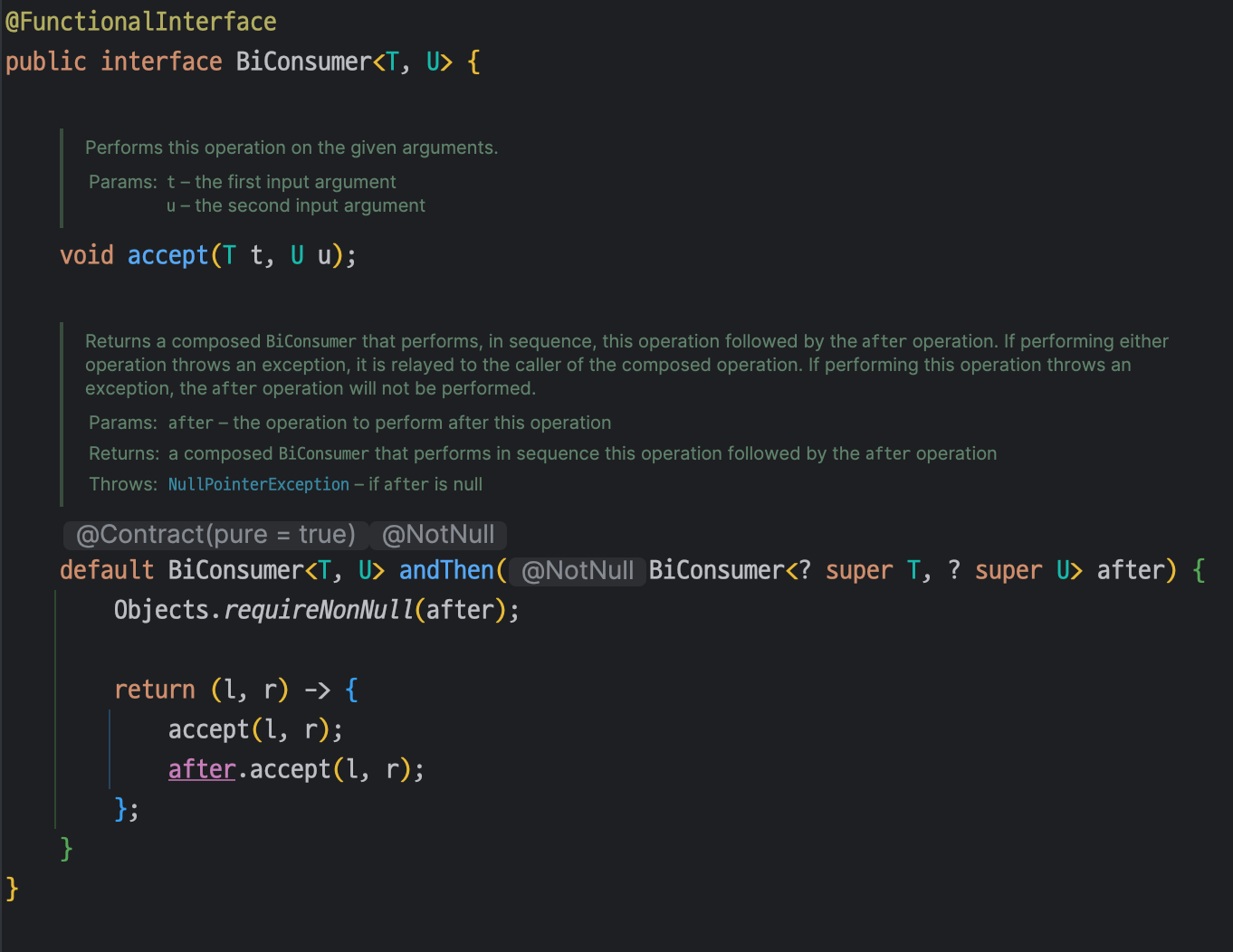
이전에 `BiFunction`을 보았다면 어느정도 예측이 될텐데 `BiConsumer`는 두 개의 입력값을 받아서 처리만 하고 아무 것도 반환하지 않는 함수형 인터페이스이다.
@Test
@DisplayName("thenAcceptBoth 으로 작업 결합하기")
void thenAcceptBoth() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> orderFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> orderItem(orderNo));
CompletableFuture<String> deliveryFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(this::getDeliveryStatus);
orderFuture.thenAcceptBoth(deliveryFuture, this::updateDeliveryStatus);
}
private String getDeliveryStatus() {
return "배송중";
}
private void updateDeliveryStatus(final String item, final String status) {
System.out.println(item + " -> " + status);
}
주문 정보와 배달 상태를 비동기로 가져온 뒤 `thenAcceptBoth`를 통해서 새로운 문자열을 출력한다. 그리고 이 작업에서 어떠한 반환값도 가지지 않은것을 확인할 수 있다.
📌 thenApply vs thenCompose
그렇다면 `thenApply` 와 `thenCompose`는 되게 비슷해 보이는데 뭐가 다른걸까?
일단 2개의 메서드 모두 후속 작업을 연결한다는 점에서는 공통점이라고 할 수 있다.
하지만 `thenApply` 는 단순 값을 가공하는 경우이고, `thenCompose`는 또 다른 비동기 작업을 연결하는 경우에서 차이가 있다.
CompletableFuture<String> orderFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "ORD1234");
CompletableFuture<String> result = orderFuture.thenApply(orderNo -> "주문번호: " + orderNo);`thenApply`는 orderNo를 받아서 문자열을 가공만 하고 있다. 즉, 값을 반환하고 있다.
CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> "ORD1234")
.thenCompose(this::getOrderNameAsync); // 리턴: CompletableFuture<String>
반면 `thenCompose`는 비동기 작업 자체를 반환한다. 그러므로 비동기 작업의 호출 결과가 필요한거라면 `thenApply`, 비동기 작업의 결과를 결합한 최종 결과가 필요한 경우 `thenCompose` 메서드를 사용하는 것이 적절할 것 같다.
Parallel Execution
📌 allOf
allOf 메서드를 사용하면 여러 가지의 `Future` 작업을 병렬로 처리할 수 있다. `allOf` 에 인자로 제공되는 모든 `Future`의 처리가 완료될 때까지 대기했다가 모두 완료되었을 때 후속 작업을 실행하게 된다.

메서드 시그니처를 살펴보면 `CompletableFuture` 를 가변 인자로 받고 있는 것을 볼 수 있으며 `CompletableFuture<Void>` 를 반환하고 있는 것을 알 수 있다. 즉, 병렬 처리는 가능하지만, 모든 `Future` 의 결과를 결합한 결과값을 반환할 수 없다는 한계가 있다.
/**
* 사용자 정보, 주문 내역, 결제 상태를 각각 비동기로 조회하고 모두 완료되었을 때 통합 응답 생성
*/
@Test
@DisplayName("allOf 콜백 조합하기")
void allOfTest() throws Exception{
CompletableFuture<String> userFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
sleep(2000);
System.out.println("userFuture");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return "사용자: WooJJam";
});
CompletableFuture<String> orderFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
sleep(2000);
System.out.println("orderFuture");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return "주문: 아이폰 16";
});
CompletableFuture<String> paymentFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
sleep(1000);
System.out.println("paymentFuture");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return "결제: 완료";
});
CompletableFuture<Void> allFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(userFuture, orderFuture, paymentFuture);
allFuture.get();
assertThat(userFuture.isDone()).isTrue();
assertThat(orderFuture.isDone()).isTrue();
assertThat(paymentFuture.isDone()).isTrue();
String result = Stream.of(userFuture, orderFuture, paymentFuture)
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.joining(" "));
assertThat("사용자: WooJJam 주문: 아이폰 16 결제: 완료").isEqualTo(result);
}
join 메서드를 활용하면 앞서 언급한 `allOf` 의 한계를 극복할 수 있다. 하지만 `Future`의 작업이 정상적으로 완료되지 않은 경우 런타임 시점에 예외가 발생할 수 있다는 점을 고려해야 한다. 그러니 반드시 예외처리가 필요하다.
다음 블로깅 주제는 `CompletableFuture` 로 예외처리를 하는 방법에 대해서 작성해보겠다.
'Backend > Spring Boot' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 자바와 스프링의 비동기 처리 - 2편: CompletableFuture의 예외 처리와 타임 아웃 (4) | 2025.08.01 |
|---|---|
| 스프링 이벤트를 발행하여 트랜잭션과 관심사 분리하기 (2) | 2025.04.29 |
| 동시성 문제에 대한 고찰, 점진적으로 접근하기 (0) | 2025.03.17 |